Local AI Engine
What is llama.cpp?
Section titled “What is llama.cpp?”llama.cpp is the engine that runs AI models locally on your computer. Think of it as the software that takes an AI model file and makes it work on your hardware - whether that’s your CPU, graphics card, or Apple’s M-series chips.
Originally created by Georgi Gerganov, llama.cpp is designed to run large language models efficiently on consumer hardware without requiring specialized AI accelerators or cloud connections.
Why This Matters
Section titled “Why This Matters”- Privacy: Your conversations never leave your computer
- Cost: No monthly subscription fees or API costs
- Speed: No internet required once models are downloaded
- Control: Choose exactly which models to run and how they behave
Accessing Engine Settings
Section titled “Accessing Engine Settings”Find llama.cpp settings at Settings > Model Providers > Llama.cpp:
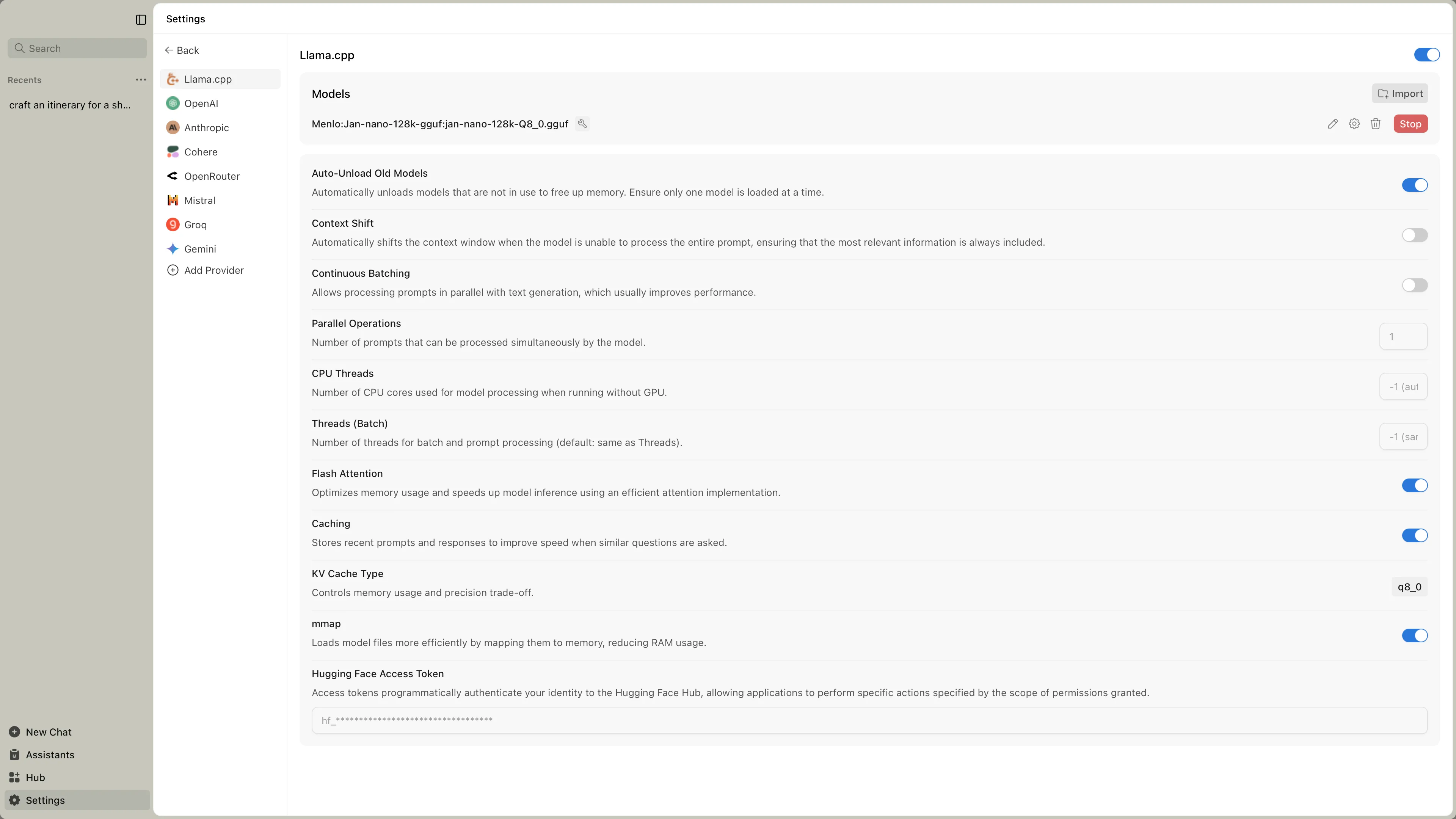
Engine Management
Section titled “Engine Management”| Feature | What It Does | When You Need It |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Version | Shows which version of llama.cpp you’re running | Check compatibility with newer models |
| Check Updates | Downloads newer engine versions | When new models require updated engine |
| Backend Selection | Choose the version optimized for your hardware | After installing new graphics cards or when performance is poor |
Hardware Backends
Section titled “Hardware Backends”Jan offers different backend versions optimized for your specific hardware. Think of these as different “drivers” - each one is tuned for particular processors or graphics cards.
NVIDIA Graphics Cards (Recommended for Speed)
Section titled “NVIDIA Graphics Cards (Recommended for Speed)”Choose based on your CUDA version (check NVIDIA Control Panel):
For CUDA 12.0:
llama.cpp-avx2-cuda-12-0(most common)llama.cpp-avx512-cuda-12-0(newer Intel/AMD CPUs)
For CUDA 11.7:
llama.cpp-avx2-cuda-11-7(most common)llama.cpp-avx512-cuda-11-7(newer Intel/AMD CPUs)
CPU Only (No Graphics Card Acceleration)
Section titled “CPU Only (No Graphics Card Acceleration)”llama.cpp-avx2(most modern CPUs)llama.cpp-avx512(newer Intel/AMD CPUs)llama.cpp-avx(older CPUs)llama.cpp-noavx(very old CPUs)
Other Graphics Cards
Section titled “Other Graphics Cards”llama.cpp-vulkan(AMD, Intel Arc, some others)
NVIDIA Graphics Cards
Section titled “NVIDIA Graphics Cards”Same CUDA options as Windows:
llama.cpp-avx2-cuda-12-0(most common)llama.cpp-avx2-cuda-11-7(older drivers)
CPU Only
Section titled “CPU Only”llama.cpp-avx2(most modern CPUs)llama.cpp-avx512(newer Intel/AMD CPUs)llama.cpp-arm64(ARM processors like Raspberry Pi)
Other Graphics Cards
Section titled “Other Graphics Cards”llama.cpp-vulkan(AMD, Intel graphics)
Apple Silicon (M1/M2/M3/M4)
Section titled “Apple Silicon (M1/M2/M3/M4)”llama.cpp-mac-arm64(recommended)
Intel Macs
Section titled “Intel Macs”llama.cpp-mac-amd64
Performance Settings
Section titled “Performance Settings”These control how efficiently models run:
| Setting | What It Does | Recommended Value | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Batching | Process multiple requests at once | Enabled | Faster when using multiple tools or having multiple conversations |
| Parallel Operations | How many requests to handle simultaneously | 4 | Higher = more multitasking, but uses more memory |
| CPU Threads | How many processor cores to use | Auto-detected | More threads can speed up CPU processing |
Memory Settings
Section titled “Memory Settings”These control how models use your computer’s memory:
| Setting | What It Does | Recommended Value | When to Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flash Attention | More efficient memory usage | Enabled | Leave enabled unless you have problems |
| Caching | Remember recent conversations | Enabled | Speeds up follow-up questions |
| KV Cache Type | Memory precision trade-off | f16 | Change to q8_0 or q4_0 if running out of memory |
| mmap | Load models more efficiently | Enabled | Helps with large models |
| Context Shift | Handle very long conversations | Disabled | Enable for very long chats or multiple tool calls |
KV Cache Types Explained
Section titled “KV Cache Types Explained”- f16: Most stable, uses more memory
- q8_0: Balanced memory usage and quality
- q4_0: Uses least memory, slight quality loss
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Section titled “Troubleshooting Common Issues”Models won’t load:
- Try a different backend (switch from CUDA to CPU or vice versa)
- Check if you have enough RAM/VRAM
- Update to latest engine version
Very slow performance:
- Make sure you’re using GPU acceleration (CUDA/Metal/Vulkan backend)
- Increase GPU Layers in model settings
- Close other memory-intensive programs
Out of memory errors:
- Reduce Context Size in model settings
- Switch KV Cache Type to q8_0 or q4_0
- Try a smaller model variant
Random crashes:
- Switch to a more stable backend (try avx instead of avx2)
- Disable overclocking if you have it enabled
- Update graphics drivers
Quick Setup Guide
Section titled “Quick Setup Guide”For most users:
- Use the default backend that Jan installs
- Leave all performance settings at defaults
- Only adjust if you experience problems
If you have an NVIDIA graphics card:
- Download the appropriate CUDA backend
- Make sure GPU Layers is set high in model settings
- Enable Flash Attention
If models are too slow:
- Check you’re using GPU acceleration
- Try enabling Continuous Batching
- Close other applications using memory
If running out of memory:
- Change KV Cache Type to q8_0
- Reduce Context Size in model settings
- Try a smaller model